Detecting Fake News With Python and Machine Learning
Detekting Fake News With Python and Machine Learning:
In this project I will try to answer some basics questions related to the titanic tragedy using Python.
A king of yellow journalism, fake news is false information and hoaxes spread through social media and other online media to achieve a political agenda. In this data science project idea, we will use Python to build a model that can accurately detect whether a piece of news is real or fake. We’ll build a TfidfVectorizer and use a PassiveAggressiveClassifier to classify news into “Real” and “Fake”. We’ll be using a dataset of shape 7796×4 and execute everything in Jupyter Notebook.
Let’s start with defining some related terms:
TfidfVectorizer: Transforms text to feature vectors that can be used as input to estimator when TF: is term frequency and IDF: is Inverse Document Frecuency.
PassiveAggressiveClassifier: are generally used for large-scale learning. It is one of the few ‘online-learning algorithms‘. In online machine learning algorithms, the input data comes in sequential order and the machine learning model is updated step-by-step, as opposed to batch learning, where the entire training dataset is used at once. This is very useful in situations where there is a huge amount of data and it is computationally infeasible to train the entire dataset because of the sheer size of the data. We can simply say that an online-learning algorithm will get a training example, update the classifier, and then throw away the example.
DataSet: for this project we will use a dataset of shape 7796x4 will be in CSV format.
Now let’s start some coding»>
First of all like all the project we will start making our necessary imports:
import itertools
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import PassiveAggressiveClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
Second we will read our data:
df=pd.read_csv(r'C:\Data Science Portfolio\DFNWPAML\Dataset\news.csv')
Third Let’s have a look of our Data to get comfortable with it
df.shape
df.head()
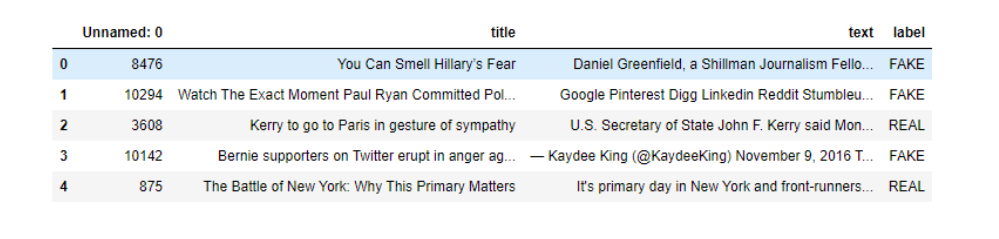
Fourth we’ll labeling our data, since we ar going to use ML algorithem labeling our data is an important part of data preprocessing for ML, particularly for supervised learning, in which both input and output data are labeled for classification to provide a learning basis for future data processing.
labels = df.label
labels.head()
0 FAKE
1 FAKE
2 REAL
3 FAKE
4 REAL
Name: label, dtype: object
Fifth we have to split our data set into traninig and testing sets so to apply ML algorithem
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df["text"], labels, test_size = 0.2, Random_state = 7)

